Polyethylene Fiber
23:19
0 comments
Polyethylene (PE) is the most widely used thermoplastic in the world. All types of polyethylene have good electrical insulation properties, high chemical resistance and good sliding properties, while their mechanical properties are generally moderate. We have found a way to crosslink the carbon chains of the plastic polymer to produce special polyethylene fibers that have a higher heat resistance than standard PE fibers.
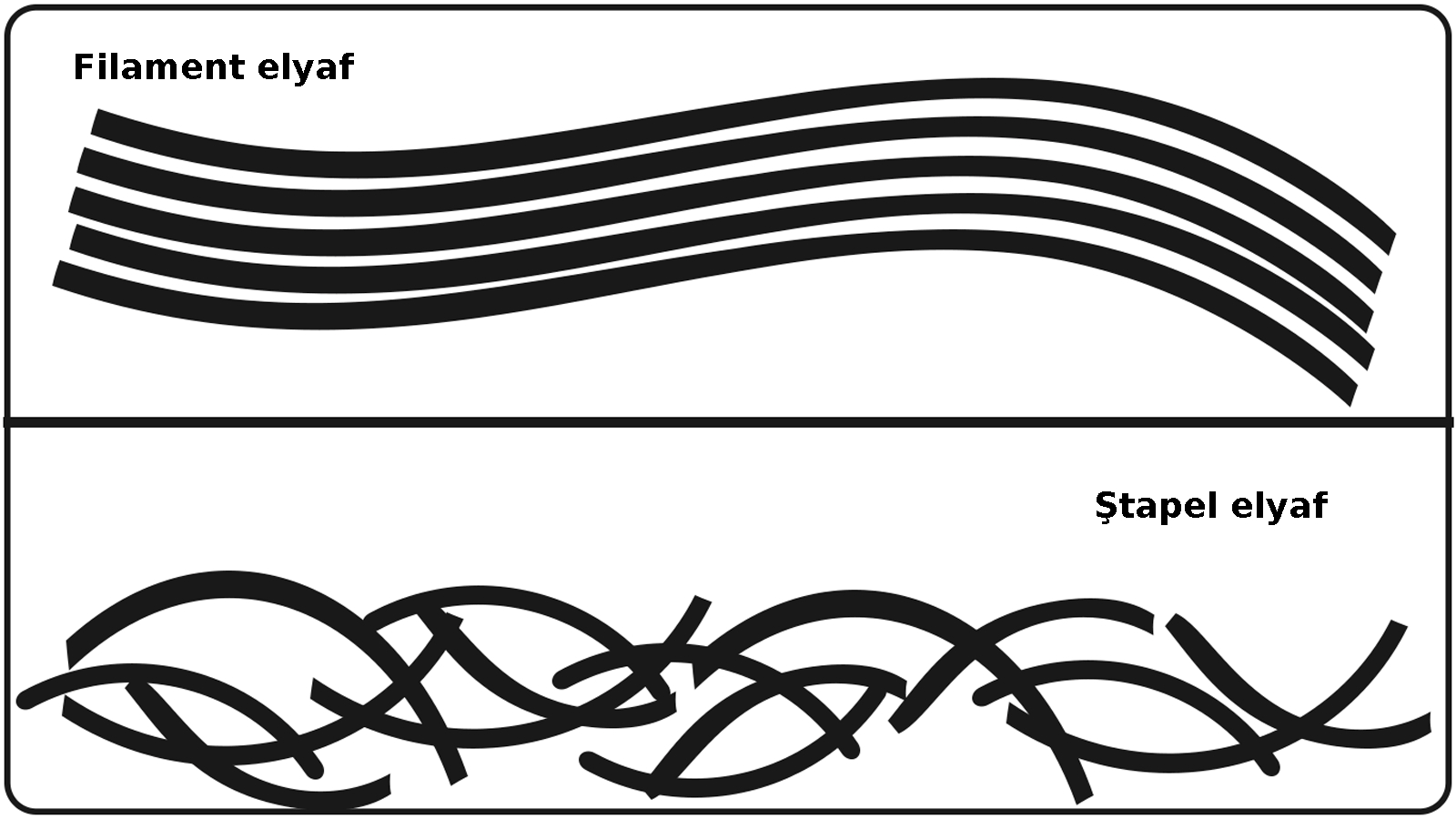
It’s a manufactured fiber made of polymerized polyethylene units. It is often a monofilament, but is also available as continuous filament yarns and as staple fiber. Polyethylene yarn cannot be dyed. It is colored by the addition of pigments and dyes to the melt at extrusion. Polyethylene can be created in several different forms. The structure is determined by the amount of branching of ethylene polymer units on the main chain. The less branching the higher the density and stronger the fiber. Typical nomenclature for polyethylene (PE) includes low density PE (LDPE), medium density PE (MDPE), high density PE (HDPE), and ultra high molecular weight PE (UHMWPE).
Polyethylene fiber properties:
- Low specific gravity (floats on water)
- Extremely low moisture regain
- Quick drying
- Mildew and insect resistant
- Chemical resistant
- Abrasion resistant
- Sunlight resistant
- Colorfast
Sample polyethylene applications:
- Geotextiles
- Outdoor furniture
- Industrial
- Filter fabric
-
Ayakkabılarda doğru numara seçimi sağlık ve kullanım ömrü açısından önem arz eder. Kesirli Ayakkabı Numaraları Ne Anlama Geliyor? 🤔 Bazı a...
-
İş sağlığı ve güvenliği için bazı işletmelerde pr ayakkabı kullanımı gereklidir. Ayakkabılarda rastladığımız "PR" terimi, İngiliz...
-
Rahat bir kullanım için ayağın genişliği ve uzunluğuna uygun ayakkabıyı seçmek son derece önemlidir. Ayakkabı Genişlik Terimleri: E, F, FX,...
-
Yeşil renk ve tonları, sarı ile mavi ışığın birleşmesi sonucu oluşur ve fotosentetik pigmentler nedeniyle bitki yapraklarında yaygın olarak ...
-
İngilizce renkler. İngilizcede renk kelimesi Amerikan İngilizcesinde "color", İngilizce İngilizcesinde "colour" olarak ...
-
Kilim Nedir? Anadolu'nun Renkli Dokusu: Kilim Motifleri ve Kültürel Değerleri Kilim dokumacılığı, Anadolu'nun köklü el sanatlarınd...
-
Lif kısaltmaları tekstilde elbise üretiminin her aşamasında kullanılır. Tekstil, Kumaş, Lif ve Elyaf Kısaltmaları : Tekstil endüstrisi, lif...
-
Elastomultiester lif yapısı. Elastomultiester , iki veya daha farklı kimyasal doğrusal makromoleküllerin iki veya daha farklı aşamada etkil...
-
Türk tekstil ve hazır giyim sektörü: yerli markaların yükselişi. Türkiye'nin lokomotif sektörlerinden biri olan tekstil ve hazır giyim...
-
Çizme ve botlarda; konç genişliği, ağız genişliği, topuk boyu, tarak genişliği ve taban iç uzunluğu. Konç, bot, çizme, ayakkabı , çorap vb...
-
Türk tekstil ve hazır giyim sektörü: yerli markaların yükselişi. Türkiye'nin lokomotif sektörlerinden biri olan tekstil ve hazır giyim...
-
Akrilik elyaf, iyi yalıtım özelliğine sahip olmasıyla öne çıkan sentetik bir lif türüdür. Akrilik Elyaf: Tanım ve Özellikler Akrilik, ( Alm....
-
Kumaş numunesi. 1) Yapılarına göre (nasıl yapıldıysa o ismi alır) a) Dokunmamış kumaşlar - Nonwoven , keçeler, kağıt telalar, elyaf, vi...
-
Ünlü Türk modacı ve tasarımcılarının kreasyonları artık dünya moda başkentlerinde sergileniyor. Türkiye'de tekstil ve moda sektörünü...
-
Farklı renk ve türdeki kumaş çeşitleri. Kumaş, ipliklerin, çeşitli yöntemlerle bir araya getirilerek oluşturduğu kaplayıcı yüzeylerd...
-
Türk ayakkabı markaları, yerli ham maddeyi mükemmel işçilik ve estetik tasarımlarla birleştiriyor. Türk malı ayakkabı ürünler, kalitesi ve e...
-
Dünyanın en meşhur modacıları. Dünyaca ünlü modacılar Her sezon önce podyumları sonra da vitrinleri süsleyen özel koleksiyonların arkas...
-
Lif kısaltmaları tekstilde elbise üretiminin her aşamasında kullanılır. Tekstil, Kumaş, Lif ve Elyaf Kısaltmaları : Tekstil endüstrisi, lif...
-
Ayakkabılarda doğru numara seçimi sağlık ve kullanım ömrü açısından önem arz eder. Kesirli Ayakkabı Numaraları Ne Anlama Geliyor? 🤔 Bazı a...
-
Naylon olarak da bilinen polyamid kumaşlar sentetik kökenli bir kumaş türüdür. Polyamid ya da naylon (Alm. Polyamidfaser, Fr. fibre ...

















































































































0 yorum:
Yorum Gönder
Merhaba, daha kaliteli bir site için yorumlarınızı bekliyoruz.